this is why spread trading is good for risk management
- You may make any transaction in the world’s financial markets, not simply bet on market direction. Most of the prominent participants in the global market are institutions, and most of those institutions have regulations on risk management and compliance. Institutions with a lower appetite for risk might benefit from spread trading because they have more cash to contribute. Spread trading is about trading a “spread,” or a “price differential,” rather than the asset itself.
- Spread trading is just a term for trading the gap between two prices. The emphasis of spread trading is on following this spread rather than the change in asset prices. Let’s examine spread trading and why it makes sense for speculators.
Spread Trading
- In the world of futures trading, “spread trading” refers to selling futures contracts while simultaneously buying them in opposite directions to balance losses. Spread trading’s appeal lies in that it monitors the spread rather than the underlying asset price and that your gains or losses are determined by the direction in which the spread moves.
- Having defined spread trading, we may explore its many subsets.
- There is spread trading between two contracts. For example, nifty June futures are one kind of futures contract that may be bought and sold.
- The difference between the basket and the index may be traded as a spread. For example, let’s say you want to invest in the Nifty stock market and use Nifty futures.
- Pair trading, or spread trading, allows you to take advantage of the inverse historical connection between two stocks, such as when you purchase Infosys and sell Hindustan Unilever.
- The first two spreads are reliable, whereas the third, based only on an empirical connection, is more prone to uncertainty. Steel and SAIL spread, such as Hindalco-aluminum spreads or Vedanta-copper spreads, are only a few examples of intraday market spreads. These are much more difficult to execute and more prone to mistakes.
Let’s talk about some of the positive aspects of spread trading today.
- Some of the primary benefits you may anticipate from spreading trading are as follows. First, you may be right about mean reversion in the long run, but in the meanwhile, the intermittent pressure brought on by growing margin pressures and financing deficits creates real challenges. So here are a few of spread trading’s benefits:
- The spread can be done without constant monitoring, unlike your price charts, which is a significant benefit of spread trading. Spreads may be traded like long-term delivery contracts, with less emphasis on real-time information.
- Therefore, program traders and other institutional traders can utilize the computational advantage to beat the market by recognizing spreads before the market can consider spreading trading.
- Mean reversion is one of the most accessible trades since it applies to stocks and spreads. Spread patterns, determined from market behavior over time, are seen by some investors as more dependable and constant.
- The need for much smaller margins is the most significant benefit of spread trading. As a result, you may take on more excellent holdings in the market but with lesser spread earnings. In addition to equity/index spreads, this holds for commodities.
- Spread trading is a less risky approach that new traders and those with a lesser tolerance for financial uncertainty may use to enter the derivatives trading market. As a result, there will be fewer errors in estimating the danger.
- Spread trading’s ability to create value even in turbulent markets, when price trading becomes riskier, is perhaps its most crucial feature.
What is Arbitrage?
- Arbitrage, in economic terms, is profit with zero downside risk. There are many opportunities to enter the market and secure a profit when the transaction is opened. Be aware that not all spread trades provide risk-free rewards. Instead, they provide an alternative setting in which danger may be reduced. Cash-futures arbitrage is a time-honored method of making guaranteed money with no risk involved. So, let’s test it out and see what happens.
- Let’s pretend you invested Rs. 2200 in 500 shares of Reliance. After researching, you learn that RIL near-month expiration futures are now selling at Rs. 2,220. A risk-free cash-futures arbitrage spread may be generated here. Your 500 shares of Reliance stock entitle you to sell two lots of RIL futures at the current price of Rs. 2,220. Your guaranteed / risk-free profit is Rs. 20 as the stock price and the futures contract expire simultaneously on the expiration day. This indicates a guaranteed return of 0.91% (20/2200).
- Remember that this is just the profit from one month’s contract, which equals an annualized return of roughly 11%. Since bank fixed deposits don’t even give you 6% per year, that’s a great return on a risk-free basis. Therefore, many major corporations and organizations like the risk-free arbitrage between cash and futures to deposit their short-term capital.
How do you calculate the minimum margin?
- The new margining structure implemented by SEBI in June 2020 provides significant relief for spread trading due to the reduced exposure to loss relative to naked transactions. For instance, a bull call spread or bear put spread on the Nifty would often result in a margin requirement that is 60–65% lower than the standard. You know that the sum of the SPAN and exposure margins are the standard margin requirement in F&O.
Frequently Asked Questions
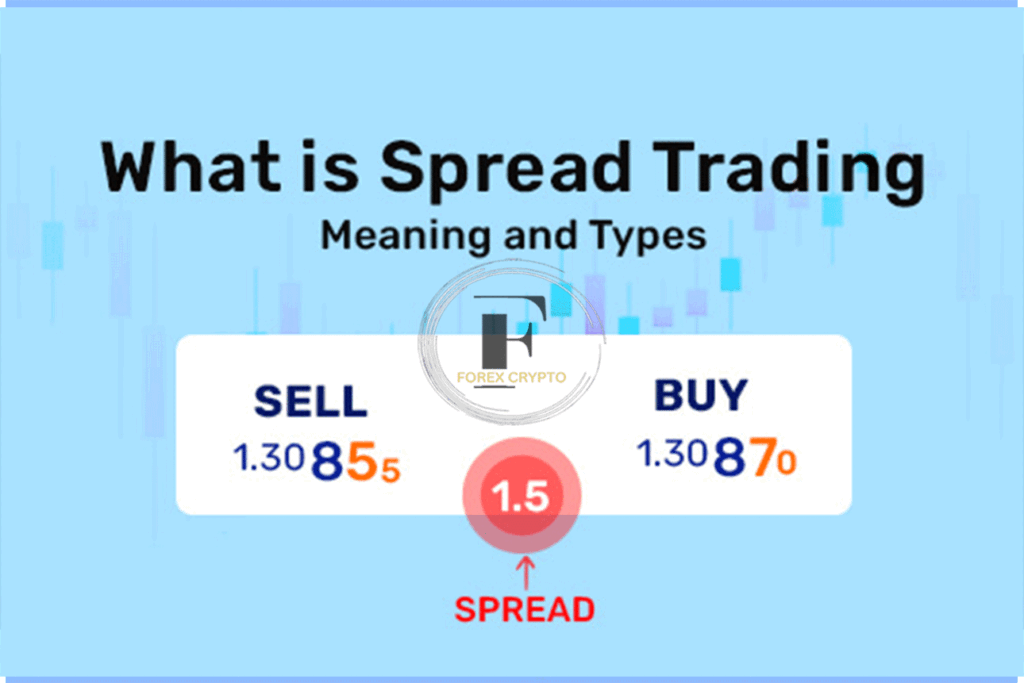
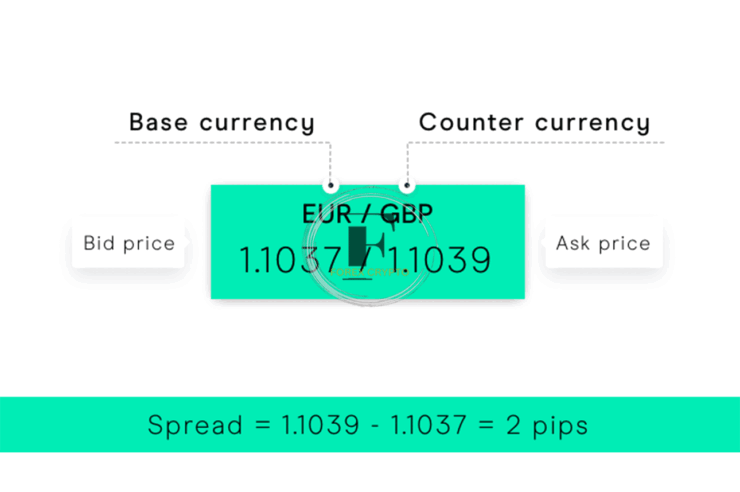
Bid-ask: What is it?
The bid-ask spread is often used to evaluate the efficiency and liquidity of a market. The asking price is the highest selling price, while the bid is the lowest buying price. It would help if you always tried to sell at the best purchase price and acquire at the best-asking price. As a general rule, the smaller this spread is, the less risk a trader has when buying or selling a stock or futures contract. The market maker’s take for providing liquidity is often the difference between the best purchase and best sale prices, known as the bid-ask spread.
How wide should a spread be?
Nothing compares to the dissemination of ideas, which varies from market to market and circumstance to circumstance. The rule of thumb is that a smaller spread is preferable.



Comments (No)