Contents
- How to Approach It?
- How to detect a flat on the chart
- How to trade in a flat
- Divergence on the MACD
- Overbought and oversold areas on the RSI
- Bounces off levels
- The MAs in a flat
- Closing thoughts
In order to provide an appropriate response to the inquiry posed in the header, we first need to define what exactly a flat is. In the canon of written works, this phenomenon is shown as a movement that is neither upward nor downward in plain evidence. To put it another way, the price is heading in the correct direction, and the maximum and lowest values for the local area are both at the same level.
The market is thought to be 70% flat, and there are only 30% of instances when there are major uptrends or downtrends. We may claim that these times are examples of price equilibrium; nevertheless, immediately after the price has broken free from the confines of the flat, we should be prepared for some kind of movement.
How to detect a flat on the chart
In an uptrend, each subsequent maximum and minimum should be higher than the one that came before it; if this is the case, we may say that the trend is bullish. It is essential to limit one’s search for ideas to those that support expansion in this context.
And a downward trend is defined by the subsequent maximum and minimum values being recorded lower than the ones that came before them. At this point, indications that the deterioration is continuing should be looked for.
Last but not least, a movement is said to be flat when there is no discernible pattern and the prices keep pushing from the resistance level and then bouncing off the support line. This kind of movement is common when there is no discernible trend. We have two options: either to purchase or to sell in this circumstance.
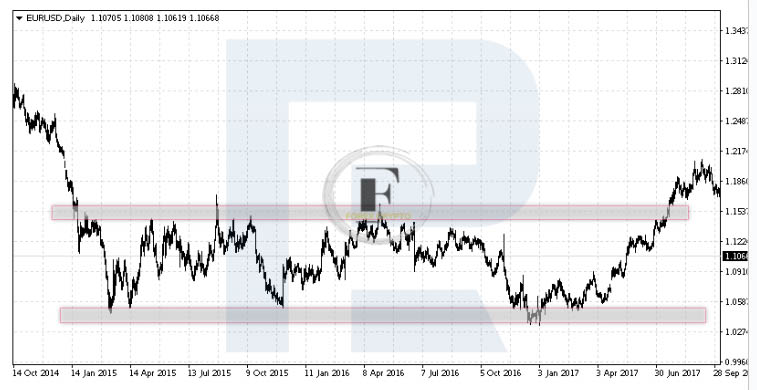
Let’s have a look at what a flat looks like on the chart of the EUR/USD currency pair. According to what we can observe, the top boundary of the channel is located close to 1.1535. After testing this line, the prices move away from it and towards the region of support that is the closest to them. They then move to the top boundary of our channel after bouncing off 1.0580 and continuing upwards.
Flat (Range) – EUR/USD chart
It is essential for us that the prices repeatedly test the support level and bounce off the resistance level; this will indicate that a flat is emerging in the market.
How to trade in a flat
It is generally agreed that a novice should follow trends like these. Beginners, as a general rule, like to average their holdings, and in a flat, prices return to the beginning levels, in contrast to significant trends. As a result, we can keep a losing position open with little effort and even gain money off of it. In any case, we need to avoid engaging in trading that is guided by our intuition and follow the guidelines of proper money management instead.
Divergence on the MACD
Moving averages perform admirably in the absence of trend divergences on the MACD when the market is moving strongly in one direction. In fact, we may go so far as to claim that the market enters a flat condition as soon as each MACD signal is triggered in succession.
First, let’s take a look at the currency pair USD/CHF. We will now move to H1 in order to employ the MACD. Chart analysis relies heavily on the ability to combine several timelines that span longer and shorter periods of time. After seeing that a flat is developing over a longer time period, the trader will now search for entry possibilities across shorter time frames.
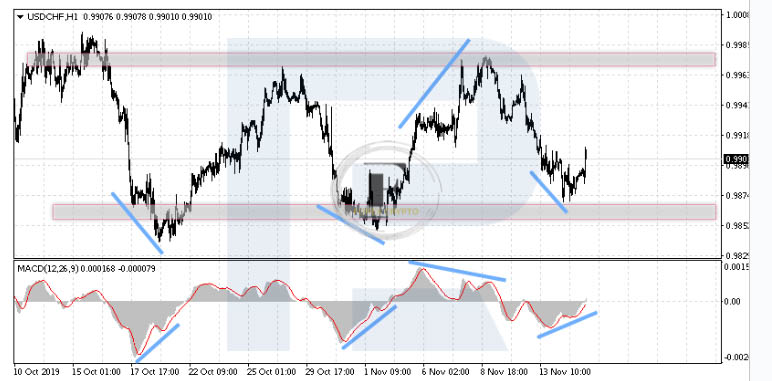
Flat (Range) – Divergence
The divergences that arise at the same time as a test of either the upper or lower boundary of our channel are the ones that need our attention. On the other hand, if the signal appears in the center of the channel, we should avoid it as much as possible.
As we can see, if one of the borders was tried and a signal occurred on the MACD, it is quite likely that the prices would return into the channel and move in the other direction. This is because it is highly likely that the prices will return to the channel after testing one of the borders. The market is entered according to the rules; for us, it is essential to wait until the signal line departs the histogram region of the indicator before entering the market. This will serve as the point of entrance.
Overbought and oversold areas on the RSI
After the testing of the levels on the RSI that are above 80 or below 20, we may also see bounces and movement in the other direction. In addition to this, the mere sight of such formations will indicate the availability of a flat for sale.
Flat (Range) – Overbought and oversold areas
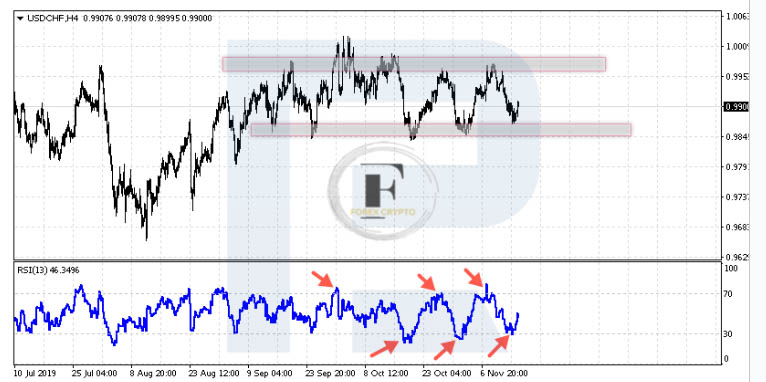
A signal to sell will be generated once the indicator readings drop back below 80 or when there is a test of the channel’s upper boundary. A purchase signal will be generated after the indicator readings move back above 20 and there is a successful test of the channel’s bottom boundary.
Bounces off levels
If we are traveling in a flat, all we need to do is swap bounces off the sides of the canal. In this scenario, a Stop order is positioned either slightly below the nearest minimum (if we buy) or substantially higher than the nearest maximum (if we sell) (if we buy).
Flat (Range) – Bounces off levels
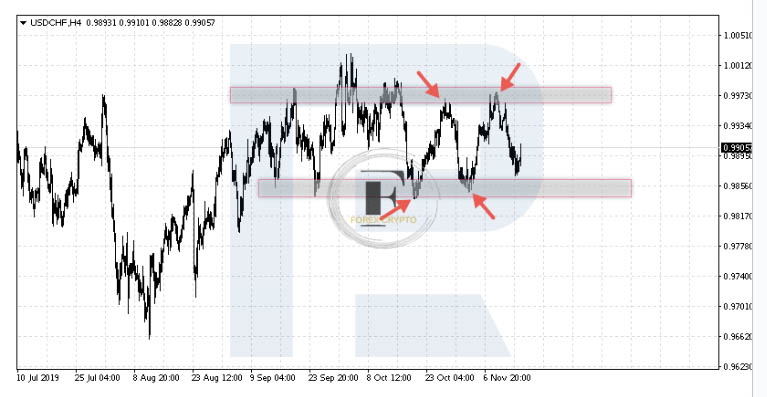
For instance, if the level of resistance is placed at 0.9905, then when the market is testing this region, we may start a selling position with a stop-loss order that is set higher than 0.9935. If the prices continue to rise, there is a good chance that they are breaking out of the channel and beginning a trend; thus, the position should be terminated as soon as possible.
The MAs in a flat
Regrettably, one of the most reliable indications of trend behaves rather randomly in such markets. Take a look one more time at the example of the USD/CHF currency pair. A bounce does not occur following the crossing of the MAs and the price returning to them, as is evident from the fact that the price continues to move in the opposite direction of our signal. On a flat, we will continually witness crosses of the MAs, and the majority of the time, the positions that are affected by these crossings will be lost.
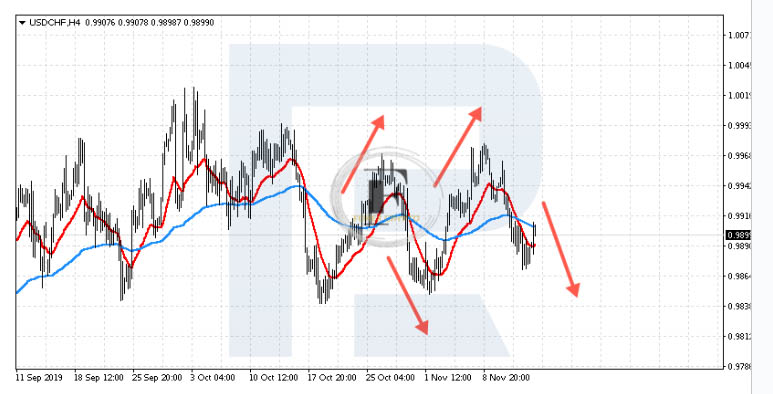
Flat (Range) – Moving Averages
Closing thoughts
Buying and selling in a flat is convenient from a number of different angles. To begin, there is a distinct demarcation between either side of the waterway. The trader is constantly aware of where the best opportunities to sell and purchase are. The risks are readily handled, and an SL has been positioned outside of the channel. The most well-known and easy-to-understand oscillators, such as the MACD and the RSI perform well; a divergence provides a distinct entry point into the market, and the signals almost always come to fruition.
The occurrence of false breakouts at the tests of the boundaries of the flat is one of the drawbacks of trading in this market. This might lead traders to assume that the flat has reached its conclusion. In addition to this, channels are not always readily discernible on the charts, and the method used to identify them is very subjective.



Comments (No)