An Explanation of Forex Spreads and Their Main Talking Points
- The purchase and sale prices of a currency pair are used to calculate spreads.
- The costs are calculated using the currency spreads and the lot sizes.
- Spreads in forex trading might change. Thus, it is important to check the information your trading platform provides.
Because they are the principal expense involved in trading currencies, traders must have a solid understanding of foreign exchange spreads. In this article, we will discuss how forex spreads operate how to calculate expenses, and keep an eye on changes in the spread to achieve the greatest possible level of success in your trading endeavors.
WHAT EXACTLY IS ENTAILED IN A FOREX SPREAD?
Forex, like any other market, has something called a spread. A spread is the price difference between the two different markets in which a trader may buy or sell an underlying asset. Traders experienced with stocks and shares will refer to this as the “Bid” in both contexts: Ask spread.
An example of the foreign exchange spread computed for the EUR/USD currency pair is shown below. We will begin by locating the purchase price, which is 1.13398, and then we will deduct the sale price, which is 1.3404. Following the completion of this procedure, the reading that we are left with is 00006. Traders need to remember that the value of one pip is determined on the EUR/USD pair by looking at the fourth number following the decimal point. This results in the final spread being computed as 0.6 pips.
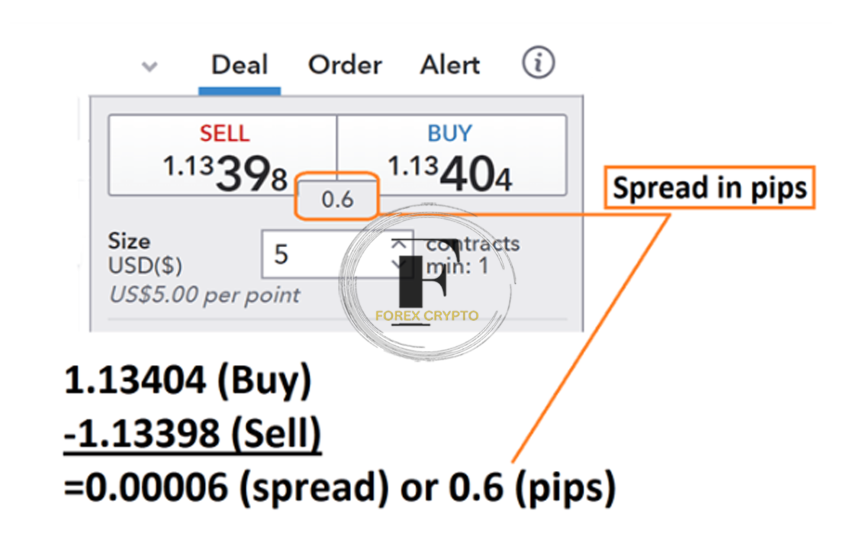
Now that we understand how to compute the spread in pips let’s look at the real cost that traders are subjected to.
HOW TO WORK OUT THE FOREX SPREAD AND COSTS IN CALCULATORS
It is important to remember that the spread of a currency pair is simply the asking price minus (or minus) the bid price before we can compute the spread cost. Therefore, using the previous example, 1.13404-1.13398 is 0.00006, or 0.6 pip difference.
Based on the above prices, the current purchase price for the EUR/USD is 1.13404, and the sale price at which we may complete the transaction is 1.13398. This indicates that a trader will be subject to a spread of 0.6 pips as soon as our deal opens.
Now that we have this value, we need to multiply it by the cost of one pip while also considering the total number of lots that were traded to calculate the entire cost of the spread. A total cost of $0.6 would be incurred when trading a 10k lot of EUR/USD. This cost would be calculated as 0.00006 (0.6 pips) multiplied by 10,000 (10k lot). If you were trading a regular lot, equal to 100,000 units of currency, the cost of your spread would be 0.00006 pips, equal to 0.6 pips multiplied by 100,000, which is $6.
You will need to change the currency of your account to dollars if it is denominated in another currency, such as the British pound.

UNDERSTANDING A HIGH SPREAD AND A LOW SPREAD
It is essential to remember that the spread on foreign exchange might shift between a “high spread” and a “low spread” within a single trading day.
This is because several variables may affect the spread, such as volatility or liquidity. You will find that the gap between certain currency pairings, such as those about developing markets, is wider than the spread between major currency pairs. Compared to currencies of developing markets, your main currency pairs trade in much larger quantities. According to a standard set of market characteristics, higher transaction volumes often result in smaller spreads.
In addition, it is good knowledge that trade liquidity may become scarce, and spreads can expand in the time leading up to significant news events and between trading sessions.
Widespread use
The spread shows the difference between the bid and the asking prices, and a big spread indicates that the difference is significant. The spread for emerging market currency pairs is often rather significant compared to major currency pairings.
A spread much wider than average often points to either high levels of market volatility or low levels of liquidity caused by trading outside of regular market hours. Spreads may become much wider before news events or at times of major shocks, such as Brexit or the US elections.
A modest spread
When referring to the difference in price between the bid and the ask, it is said to have a low spread when that difference is relatively tiny. Trading when narrow spreads, such as during the big forex sessions, is more profitable than trading at other times. When the spread is low, volatility is often low, and a low spread typically accompanies good liquidity.
KEEPING A WATCHFUL EYE OUT FOR MODIFICATIONS TO THE SPREAD
The stock market is often volatile just after major news events. Releases on the economic calendar occur at random intervals, and the degree to which expectations are realized or not may significantly impact the volatility of market values. Large liquidity providers are in the same position as ordinary traders in that they do not know the outcomes of news events before they are made public. As a result, they attempt to mitigate some of the risks associated with their positions by increasing the spreads.
Spreads have the potential to result in margin calls.
If you are presently holding a trade and the spread significantly widens, you risk having your position halted from under you or receiving a margin call. During periods in which spreads are expanding, the only way to protect yourself is to restrict the amount of leverage employed in your account. During periods in which the spread is increasing, it is occasionally advantageous to wait on trade until the spread has become more narrow.




Comments (No)