QUANTITATIVE EASING EXPLAINED: MAIN TALKING POINTS
HOW DOES QUANTITATIVE EASING WORK?
THE QUANTITATIVE EASING POLICY OF THE FEDERAL RESERVE BANK OF THE UNITED STATES (FED)
TOTAL ASSETS HELD BY THE FEDERAL RESERVE BANK
MODIFICATIONS MADE TO THE FED’S BALANCE SHEET AS A RESULT OF QUANTITATIVE EASING
THE QUANTITATIVE EASING POLICY OF THE BANK OF JAPAN (BOJ)
THE BANK OF ENGLAND (BOE) QUANTITATIVE EASING POLICY
THE QUANTITATIVE EASING PLAN OF THE EUROPEAN CENTRAL BANK (ECB)
NEGATIVE EFFECTS OF QE: BALANCE SHEET USE AND DIMINISHING RETURNS
THE REPERCUSSION THAT QUANTITATIVE EASING HAS ON DIFFERENT CURRENCIES
QUANTITATIVE EASING EXPLAINED: MAIN TALKING POINTS
- Because interest rates were so close to zero, the Federal Reserve experimented with a new policy instrument called quantitative easing.
- After several years of quantitative easing, the Bank of Japan has seen a decline in its economic and financial returns.
- Similarly, the European Central Bank (ECB) has participated in long-term refinancing operations (LTROs) as a type of quantitative easing, however, the viability of these operations still needs to be determined.
HOW DOES QUANTITATIVE EASING WORK?
When other, more conventional techniques of stimulating the economy have been exhausted, central banks turn to quantitative easing, often known as QE for short, This is a tool of monetary policy that central banks commonly utilize, By purchasing assets, most commonly government bonds, from its member banks, the central bank effectively increases the amount of money available to consumers and businesses in the economy.
Because of the increasing supply, the cost of money has decreased, making it more affordable for firms to take out loans to finance their development, This has an impact comparable to the typical interest rate reductions for shorter-term loans that central banks implement, however, depending on what they acquire, such efforts may decrease the cost of loans with substantially longer terms, This may directly impact loans for real estate, automobiles, and even small enterprises.
THE QUANTITATIVE EASING POLICY OF THE FEDERAL RESERVE BANK OF THE UNITED STATES (FED)
As the Federal Reserve is the central bank of the United States, it is the Federal Reserve’s responsibility to provide the country with a monetary and financial system that is safer, more flexible, and more stable. This is sometimes summed up as a stated dual mission of maintaining a constant inflation rate while maintaining a low unemployment rate. For the Federal Reserve to accomplish these goals, it has been provided with a set of monetary policy instruments that allow it to affect both the value of the US dollar and the amount of money available in the nation. Although increasing and decreasing the federal funds rate is the most well-recognized instrument, investors have been more interested in the balance sheet of the central bank due to its increased relevance.
TOTAL ASSETS HELD BY THE FEDERAL RESERVE BANK
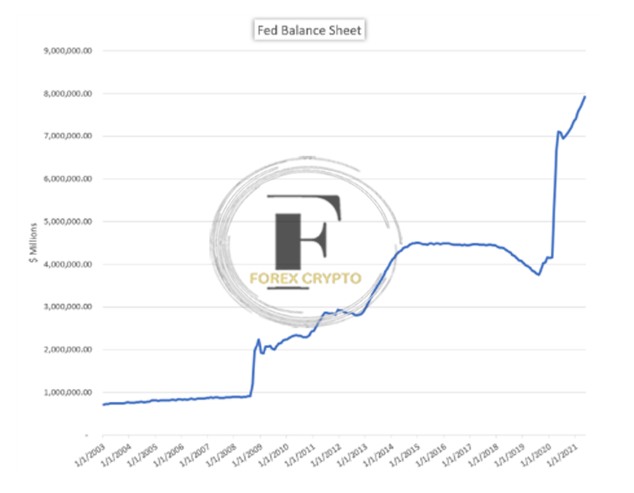
FRED is the source.
To put it another way, the Federal Reserve’s balance sheet is the same as any other balance sheet, In the case of the Federal Reserve, it is used to keep track of the collection of individual assets and liabilities that span all of the Fed’s bank branches, The bank may employ these assets and liabilities as an unorthodox or supplemental monetary policy instrument when interest rates are already low and impart little potential with additional policy efforts, This is especially useful when the bank’s other policy options are restricted.
In 2008, when the United States economy entered a recession amid the Great Financial Crisis, the Federal Reserve declared a series of interest rate cuts and began implementing them, The cutbacks, a classic example of an expansionary policy instrument, were meant to encourage consumers to increase their spending, ultimately benefiting the economy, Nevertheless, despite interest rates close to zero, the economic rebound did not take hold.
After that, in November of 2008, the Federal Reserve announced that it would begin its first round of quantitative easing, often called QE1, The news caused the Federal Reserve to make a substantial adjustment to its usual market operations, and it caused the Fed to start purchasing considerable quantities of asset- and mortgage-backed securities of a high grade, as well as treasury bills, notes, and bonds, The purchases had the effect of increasing the money supply in the US economy, which in turn lowered the costs associated with gaining access to capital, The purchase program extended from December 2008 to March 2010 and was followed by another drop in the Fed Funds rate resulting in a new range of interest rates of 0 to 0.25%, During this time, the Fed Funds rate was also lowered.
MODIFICATIONS MADE TO THE FED’S BALANCE SHEET AS A RESULT OF QUANTITATIVE EASING
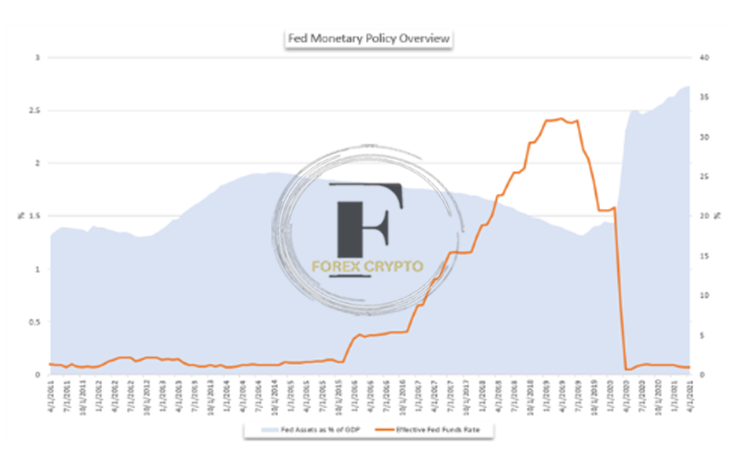
Bloomberg is the cited source.
Because the Federal Funds rate was so close to 0 and the central bank was unwilling to consider negative rates then, it had essentially used up all of its expansionary monetary policy options, As a result, quantitative easing became an essential instrument in the central bank’s toolkit to stimulate economic development and right the sinking ship that represented the economy of the United States.
Between November 2010 and June 2011, the Federal Reserve implemented a program now known as Quantitative Easing Round 2, Between September 2012 and December 2013, the Fed implemented a program now known as Quantitative Easing Round 3, The purchase programs targeted comparable assets and served to prop up perceived growth – as well as capital markets as a side effect – in the US until the central bank ultimately reversed course by increasing its benchmark rate for the first time in December 2015, at which point the central bank raised the rate for the first time.
Even though it had already begun to lower its balance sheet in 2018, we have seen discussion regarding a persistent Quantitative Tightening (cutting the balance sheet) emerge in 2019, As a result of the United States economy enjoying over a decade of economic prosperity, several officials from the Federal Reserve have urged for more normalization while supporting the gradual reduction of the bank’s balance sheet, However, the question of this extraordinary assistance has become more difficult as a result of unequal economic development as well as external dangers such as trade disputes.
THE QUANTITATIVE EASING POLICY OF THE BANK OF JAPAN (BOJ)
Another financial institution that has used quantitative easing, but with variable degrees of success, is the Bank of Japan, which serves as the country’s central bank. One of the earliest examples happened between October 1997 and October 1998, when the Bank of Japan (BOJ) acquired billions of yen worth of commercial paper to assist banks through poor growth, low-interest rates, and problems caused by bad bank loans. This was one of the first times this kind of action was taken. Despite this, growth could have been more robust.
The Bank of Japan boosted its asset purchases between March 2001 and December 2004 in response to the lackluster effect of its previous policies, The Japanese banking system received an injection of cash of 35.5 trillion yen due to this round of asset purchases, which focused on long-term government bonds, Although the purchases were only partially successful, the purchase of long-term government bonds lowered asset rates, which led to Japan’s growth being wiped out once again when the Great Financial Crisis began, Since then, the Bank of Japan has carried out many rounds of quantitative easing (QE) and qualitative monetary easing (QQE), which were mostly ineffectual, This is because the nation continues to suffer from poor economic growth despite an environment with negative interest rates.
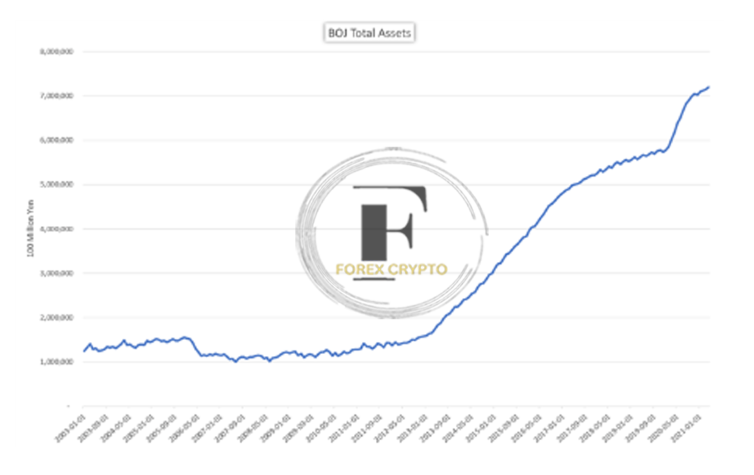
Bloomberg is the cited source.
The Bank of Japan has diversified its asset acquisitions into various forms, each of which carries a different level of quality, In addition to past acquisitions of commercial paper, the bank has amassed a sizeable ownership stake in the nation’s exchange-traded fund (ETF) market and Japanese real estate investment trusts (J-REITs).
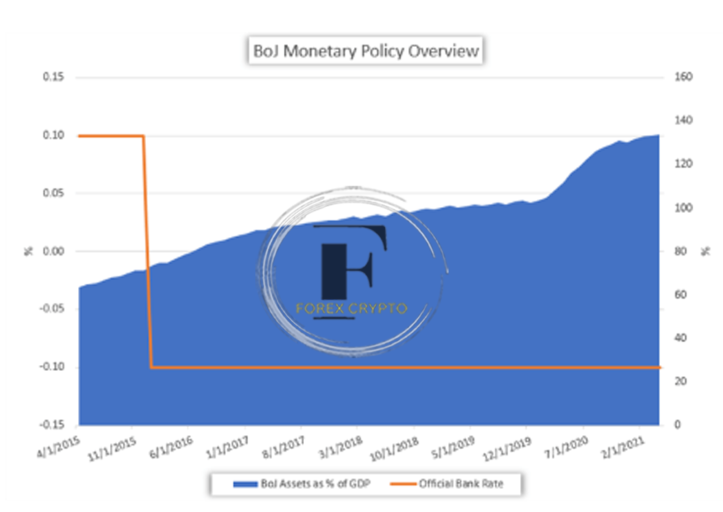
Bloomberg is the cited source.
The BOJ first started buying exchange-traded funds in 2010, and as of the second quarter of 2018, it held around 70 percent of the overall Japanese ETF market, According to Bloomberg, the Japanese central bank has become the primary stakeholder in more than forty percent of all publicly traded companies in Japan due to these extensive acquisitions, Therefore, the quality and credit rating of these holdings by the central bank is lower than that of a government-issued asset such as Japanese Government Bonds (JGBs), and they vary significantly from the holdings of the Federal Reserve in a significant way.
THE BANK OF ENGLAND (BOE) QUANTITATIVE EASING POLICY
Through its quantitative easing program, the BOE has accumulated significant quantities of local government bonds (gilts) and corporate bonds, much like the other central banks stated before, The strategy was undertaken to bolster the United Kingdom’s economy during the worst global crisis, nevertheless, it would ultimately spill over to the additional danger of political hazards posed by a vote on a Scottish Referendum, a General Election, and Brexit, At the same time, the bank has been gradually raising the rate at which it lends money overnight.
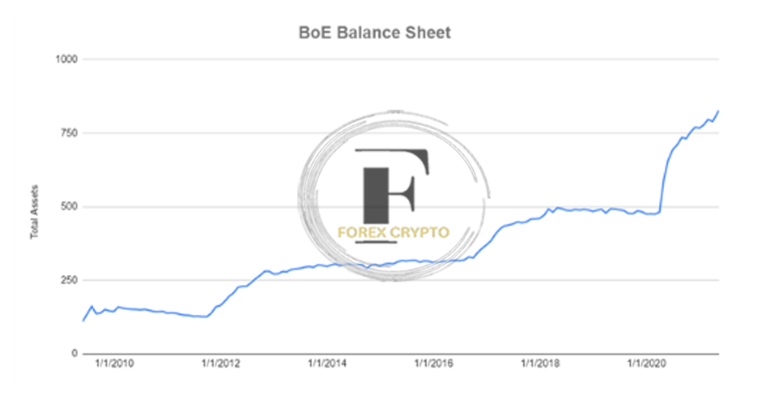
Bloomberg is the cited source.
Compared to its equivalents in the United States and Japan, the total holdings of the Bank of England in the United Kingdom are much lower, When compared to Japan’s holdings, which are equivalent to more than 100% of GDP, the Bank of England’s holdings amount to a meager 5.7% of the country’s GDP as of the beginning of 2019, This pales compared to Japan’s holdings, equivalent to more than 100% of GDP, Because the decreasing benefits from QE have yet to take effect, the bank may be able to operate more effectively in the future thanks to the relatively modest holdings.
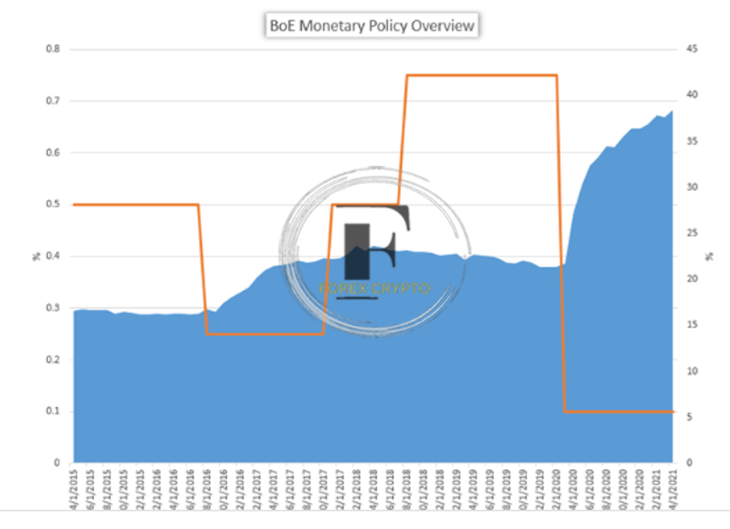
Bloomberg is the cited source.
Currently, the effectiveness of the quantitative easing policy used by the BOE is superior to that of the BOJ and is on par with that of the Federal Reserve, As a result of the continuing unpredictability caused by Brexit, the bank may choose to keep its safety net in place or even go so far as to extend its monetary policy measures, The bank will continue to commit to quantitative easing far lower than its neighbor, the European Central Bank.
THE QUANTITATIVE EASING PLAN OF THE EUROPEAN CENTRAL BANK (ECB)
The European Central Bank (ECB) is another major central bank that has embraced quantitative easing as an economic expansionary tool, however, its entry into what is generally considered conventional QE occurred much later than the Federal Reserves, During the most recent phase of its quantitative easing program, the European Central Bank (ECB) purchased almost $3 trillion worth of asset-backed securities, covered bonds, asset-backed securities, and government and corporate debt.
Between March 2015 and December 2018, purchases were made in an attempt to forestall sub-zero inflation from becoming a problem for the European Union, which was still in the process of recovering from the twin calamities of the global recession and, subsequently the Eurozone Debt Crisis at the time, According to Reuters, the rate of purchases was 1.3 million Euros per minute, equivalent to 7,600 Euros for each individual residing inside the bloc.
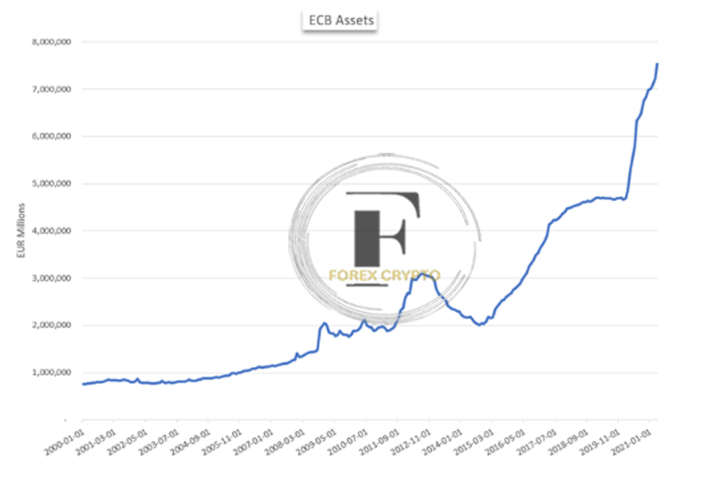
Bloomberg is the cited source.
As in Japan, the easing rounds implemented by the ECB were mainly ineffectual. Early in 2019, the bank announced another wave of easing via targeted long-term refinancing operations, often known as TLTROs. This came only a few months after the bank concluded its open-ended quantitative easing program, and it came while interest rates continued to stay at 0%. To increase bank liquidity and decrease the rates on sovereign debt, TLTROs provide banks in the Eurozone access to low-interest lending. This is done to bring down the yields on the national debt. The loans have terms ranging from one to four years in length.
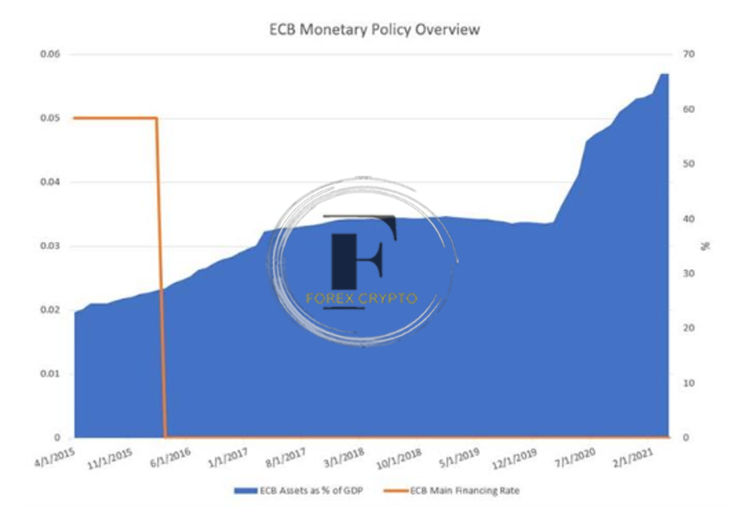
Bloomberg is the cited source.
TLTROs aim to bring about stability in the balance sheets and liquidity ratios of private banks. The bank can lend money more quickly when it has a higher liquidity ratio, which, in turn, causes interest rates to fall and should provide room for inflation. However, prolonged monetary stimulation might result in declining returns and have unfavorable repercussions in the long run.
NEGATIVE EFFECTS OF QE: BALANCE SHEET USE AND DIMINISHING RETURNS
While quantitative easing was successful for the Federal Reserve and the United States, the monetary policy instrument has been less successful for the central banks of Japan and Europe, and it has even produced certain negative outcomes, Years of expansionary policies have caused deflation in the Japanese economy, and the Japanese central bank’s balance sheet as of right now shows bears a more excellent value than the country’s GDP.
In addition, it has such a significant ownership stake in the ETF, JRIET, and government bond markets may place it at an increased risk if the economy experiences a slowdown, The Japanese central bank is now venturing into uncharted terrain in terms of monetary policy due to the failure of economic growth to materialize despite many rounds of stimulus and negative interest rates.
As a result of low inflation and slow economic development in the bloc, the European Central Bank (ECB) has seen the impact of its brand of quantitative easing have less of an impact on the European economy.
THE REPERCUSSION THAT QUANTITATIVE EASING HAS ON DIFFERENT CURRENCIES
The practice of quantitative easing, in its most basic form, contributes to an increase in the available supply of a currency, A move of this kind ought to bring about a decline in the price of that currency in accordance with the fundamental laws of supply and demand, However, since currencies are always exchanged in pairs, any decline in the value of one currency will always be measured by its other currency.
Because the present environment surrounding monetary policy is leaning toward abundant supply and dovish tones, only a few currencies announce unequivocal strength, Recent gains in strength have been achieved via an almost best-of-the-rest attitude, in which a dovish shift from one central bank is followed soon afterward by dovishness from another bank, This has resulted in the accumulation of strength, These covertly competing policies can potentially escalate into open hostilities, leading to what is known as a “currency war.”
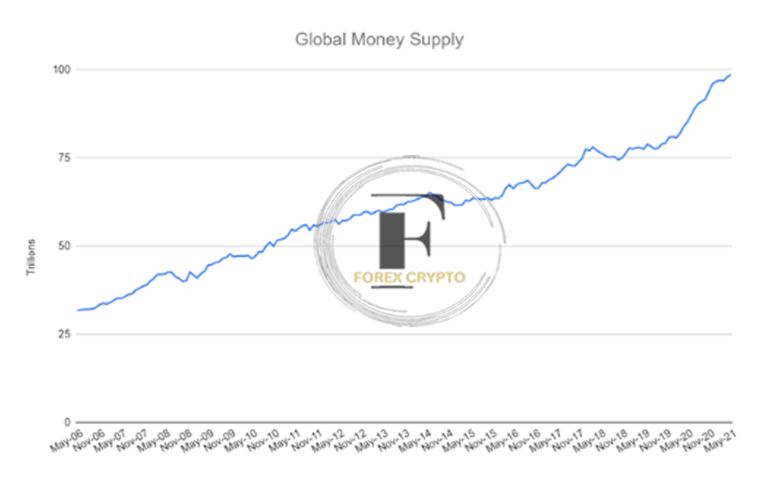
Bloomberg is the cited source.
As a direct result, the total amount of money available worldwide has increased dramatically, but the relative value of different currencies continues to fluctuate. The present environment surrounding monetary policy has transformed differences in approach into a comparison of dovishness to a considerable extent. Few of the major central banks have a hawkish stance on monetary policy, and an even smaller percentage of those institutions have any intentions to increase their key interest rate. Instead, policymakers have turned to rounds of capital injection as quantitative easing is gaining appeal as a tool for monetary policy. It is still being determined whether or not it will continue to be a permanent one.



Comments (No)