What may be found on this page?
- MAIN DISCUSSION POINTS CONCERNING FOREIGN EXCHANGE INTERVENTIONS CONDUCTED BY CENTRAL BANKS
- WHAT EXACTLY IS MEANT BY THE TERM “FOREIGN EXCHANGE INTERVENTION”?
- HOW TRADERS IN FOREIGN EXCHANGE CAN PROFIT FROM CENTRAL BANK INTERVENTION
- WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF CENTRAL BANKS ‘ INTERVENTION IN THE FOREIGN EXCHANGE MARKET?
- WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF THE CURRENCY INTERVENTION?

MAIN DISCUSSION POINTS CONCERNING FOREIGN EXCHANGE INTERVENTIONS CONDUCTED BY CENTRAL BANKS
To maintain the value of their respective national currencies, central banks will often decide that it is essential to interfere in the foreign exchange market. To do this, central banks may either purchase or sell their foreign exchange reserves, or they can merely say that a particular currency is either undervalued or overvalued and then leave the foreign exchange market players to handle the remainder of the process. This article examines the many methods by which central banks intervene in financial markets and the crucial information that traders need to consider before engaging in financial transactions.
WHAT EXACTLY IS MEANT BY THE TERM “FOREIGN EXCHANGE INTERVENTION”?
Intervention in the foreign exchange market refers to the procedure by which a central bank will purchase or sell foreign currency to either maintain stability in the exchange rate or rectify misalignments in the foreign exchange market, This is often followed by a later adjustment, made by the central bank, to the money supply to compensate for any unfavorable knock-on effects that may have been felt in the local economy.
The process referred to as “sterilized intervention” will be explored later on, along with the many other strategies for intervening in currency markets, It was stated above.
HOW TRADERS IN FOREIGN EXCHANGE CAN PROFIT FROM CENTRAL BANK INTERVENTION
Traders must remember that when a central bank intervenes in the foreign exchange market, the price movements may be turbulent, As a result, it is essential to determine an acceptable risk-to-reward ratio and to use sound risk management practices.
When the current trend in the foreign currency market moves in the opposite direction of where the central bank wants the exchange rate to be, central banks are likely to interfere, Consequently, trading around central bank intervention is similar to trade reversals.
In addition, the foreign exchange market tends to anticipate intervention from the central bank, which means that it is not unusual to see movements that go counter to the long-term trend in the minutes leading up to intervention from the central bank, Because there is no assurance of a particular outcome, traders cannot wait for a new trend to develop before they place a transaction.
WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF CENTRAL BANKS ‘ INTERVENTION IN THE FOREIGN EXCHANGE MARKET?
Most central banks think that intervention is required to either boost the economy or maintain a desirable level of the currency’s exchange rate, Suppose the value of the local currency rises to a point that makes exports from the country more costly to countries in other parts of the world, In that case, central banks will often sell their currency reserves to purchase foreign currency, Because of this, central banks purposefully manipulate the exchange rate so that they might benefit their economies.
The following is an example of a successful intervention by a central bank in reaction to the strength of the Japanese Yen compared to the US dollar: The Bank of Japan believed that the exchange rate was unfavorable, and as a consequence, they moved quickly to interfere to cause a depreciation of the Yen, This, in turn, caused the USD/JPY pair to go upward. The intervention occurred at the time shown by the blue circle, and the impact started to become apparent not long after that.

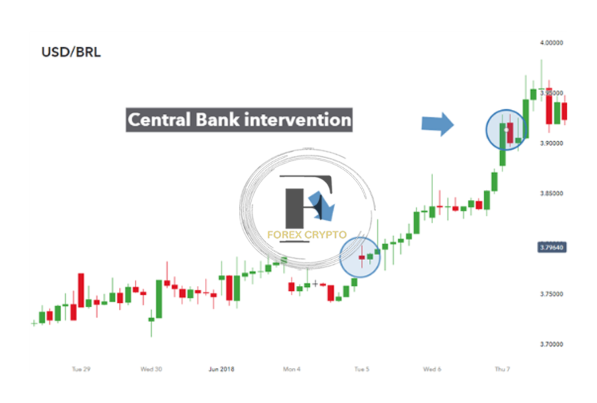
There are exceptions to the rule that even while most interventions by central banks are effective, sometimes they are not, The USD/BRL (Brazilian Real) currency pair has an illustration of a currency intervention example in the chart that follows, The figure illustrates both times the Brazilian Central Bank had to step in to prevent further depreciation of the Brazilian Real, As the dollar’s value proceeded to climb to ever-higher levels, it is abundantly evident that none of the two possible outcomes succeeded in quickly boosting the value of the Brazilian real compared to the US dollar.
WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF THE CURRENCY INTERVENTION?
The options available to central banks regarding the kinds of interventions to implement are diverse, These may take the form of either direct or indirect action. Direct intervention, as its name indicates, immediately impacts the foreign exchange market. In contrast, indirect intervention accomplishes the central bank’s goals via less intrusive methods. Some instances of direct and indirect involvement are shown below:
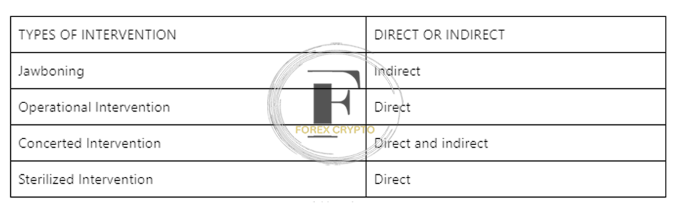
- When most people talk about central bank action, they often refer to “operational intervention.” The central bank will purchase and sell foreign money and local currency to achieve the desired exchange rate level during this process, The sheer magnitude of the transactions moves the market.
- This is an example of an indirect form of foreign exchange intervention known as “jawboning,” in which a central bank threatens to act in the market if the value of the local currency reaches a specific level deemed undesirable, As its name indicates, this approach focuses more on communication than on direct involvement, Because the central bank is prepared to step in, traders take it upon themselves to work together to bring the currency back to levels that are seen to be more acceptable.
- Concerted Intervention: This is a mix of jawboning and operational intervention, and it is most successful when numerous central banks simultaneously raise the same worries about exchange rates, One of the world’s central banks may engage in some operational intervention to move the exchange rate in the desired direction if many central banks ramp up their threats and threats of action.
- Sterile intervention entails two measures being taken by the central bank to impact the exchange rate while at the same time maintaining the status quo of the monetary base. This kind of intervention is referred to as “sterilized intervention.” This includes two separate transactions: the first is the sale or purchase of foreign currency, and the second is an open market operation consisting of the sale or purchase of government securities of the same magnitude as the first transaction.




Comments (No)